Voyages for a new world order
Exhibition highlights Zheng He's extraordinary journeys, Zhao Xu reports.


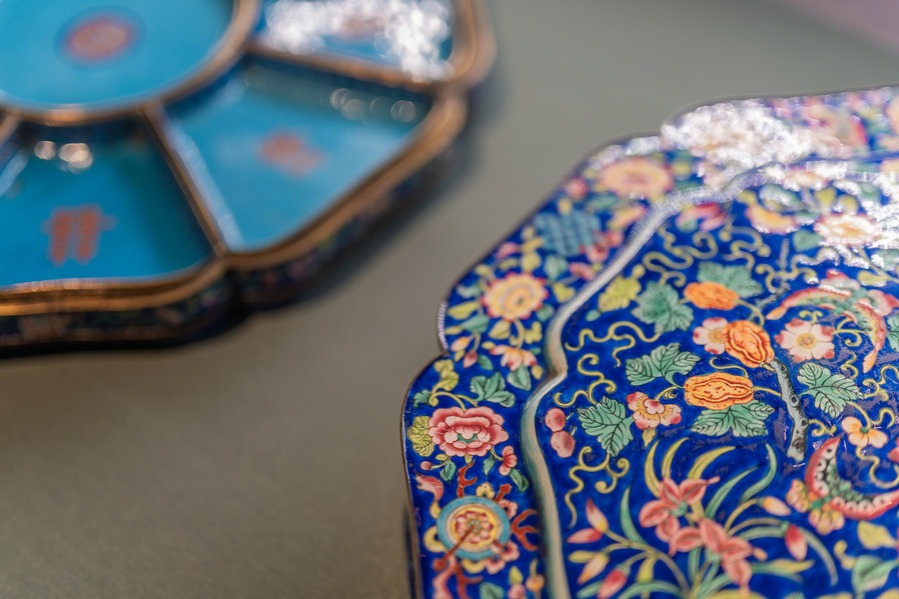
A jade pendant shaped like a pepper, adorned with gilded silver leaves; a yellow-glazed snuff bottle crafted in the form of an ear of corn; and a purple clay teapot resembling a plump pumpkin — these charming objects are among the treasures on display at The World-view of the Great Ming Dynasty, an exhibition running until July 20 at the Nanjing Museum in East China's Jiangsu province.
Their inclusion is no coincidence: Pepper, corn and pumpkin were all introduced to China around the 16th century, arguably brought by the Portuguese, who then dominated maritime trade.
These exotic plants, once unfamiliar, gradually took root in Chinese soil — both literally and culturally.
Yet, long before all that, there was the legendary Chinese seafarer Zheng He, whose seven voyages between 1405 and 1433 were unmatched in scale and ambition until Vasco da Gama's historic expedition from 1497 to 1499 — more than 60 years later.
"What we have here is a piece of tangible proof of the legacy of Zheng He — Ming (1368-1644) China's, and arguably Chinese history's, greatest maritime explorer," says Gao Jie, the exhibition's curator, gesturing toward a rubbing of a stone stele on display.
Unearthed in 1911 in Galle, a port city on the southwestern coast of Sri Lanka, the stele records Zheng's offerings and donations at a local shrine during a stop on his second voyage, and features inscriptions in Chinese, Persian and Tamil.
"Far more than feats of navigation, Zheng He's voyages were acts of cultural diplomacy — designed to elevate the Ming Dynasty's stature across the diverse societies of the Indian Ocean world," Gao adds.
Stretching from China to the east coast of Africa — where shards of Chinese porcelain dating back to the 15th century have been unearthed — Zheng's voyages followed meticulously planned routes through Southeast Asia, South Asia and the Middle East.