Haiyang heat exchange cuts carbon emissions, air pollution
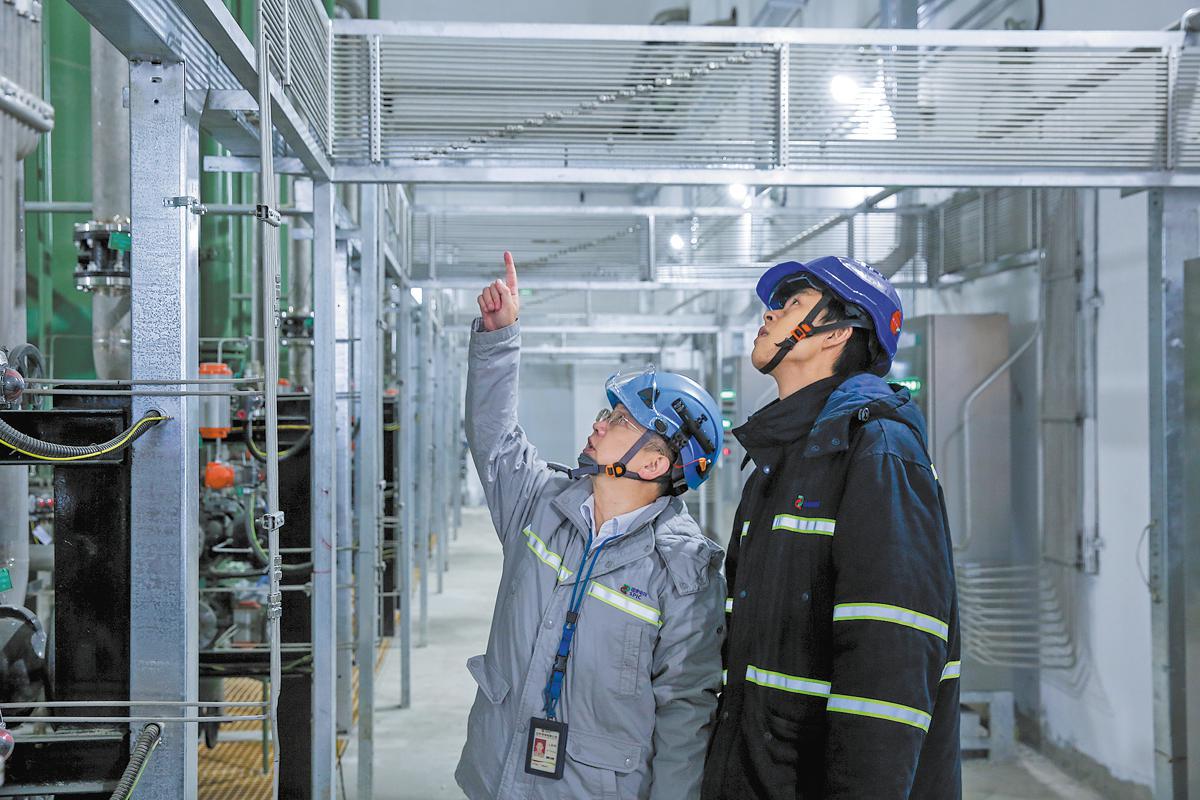


The process of nuclear fission creates a lot of heat that can be lost and wasted if not for the process of heat exchange.
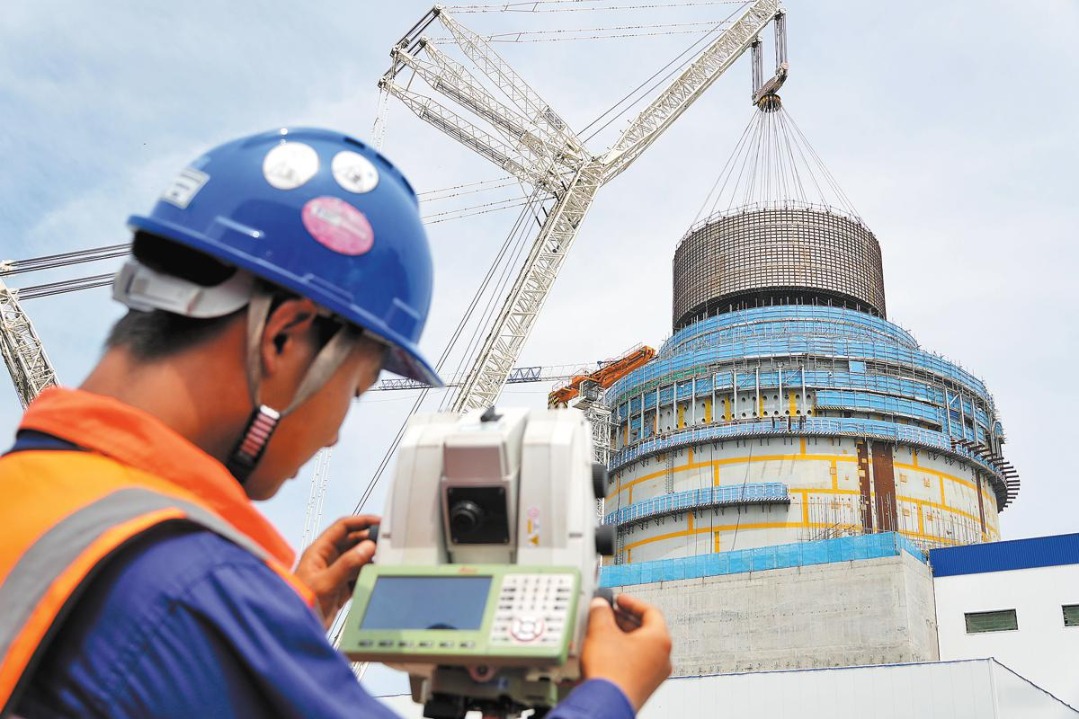
At the Haiyang Nuclear Power Plant in East China's Shandong province, heat produced by the two working reactors there is being used to heat the homes of the residents in Haiyang and nearby Rushan county — that's over 1 million people.
An added byproduct of using this heat exchange is that less heat is required to be produced by coal, reducing carbon emissions and air pollution at the same time.
Shandong Nuclear Power Co, operator of the facility, said it plans to expand its heat coverage next year to Qingdao over 100 kilometers away.
Launched in 2019, the first phase of the nuclear energy heating project, dubbed "Warm-U-Clear No 1", provided carbon-free heating to buildings covering a total floor area of 700,000 square meters, followed by the second phase in 2021 that covered 5 million sq m.
Its third phase went into operation in 2023 with a capability to serve 12.5 million sq m.
To date, the nuclear energy heating project has supplied 14.32 million gigajoules of heat, equivalent to saving standard coal consumption by approximately 1.29 million metric tons and reducing carbon dioxide emissions by 2.36 million tons, according to Shandong Nuclear Power Co.
It has also cut sulfur dioxide emissions by 15,000 tons, and nitrogen oxides by 14,000 tons, it said.
The transition to carbon-free heating has had a substantial impact on the air quality in Haiyang and Rushan. In Haiyang, the average concentration of PM10 particulate matter has decreased by 43 percent during the heating season compared to levels before the adoption of nuclear heating, while Rushan has seen an 8.7 percent reduction.
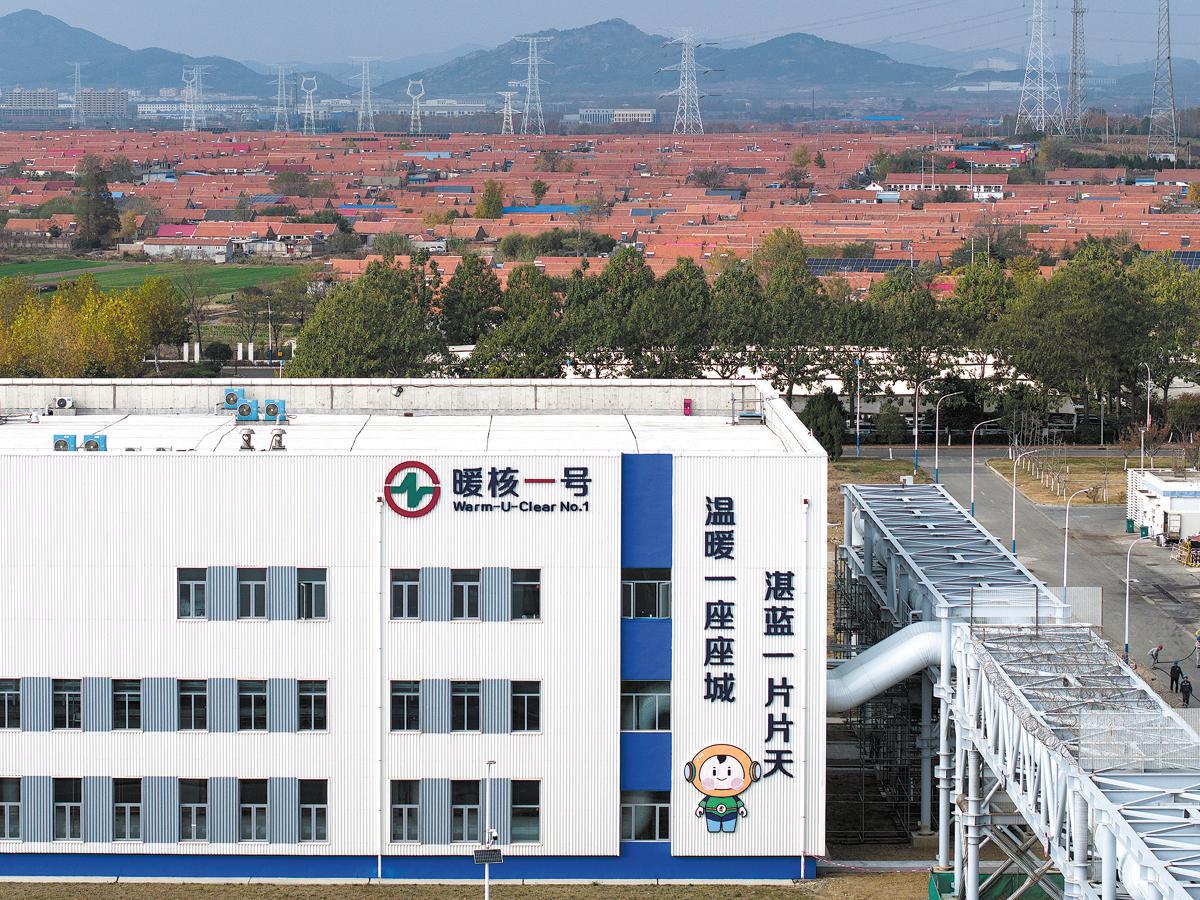

Haiyang has experienced a 13.7 percent drop in nitrogen dioxide, with Rushan's falling by 12.8 percent. Previously, both Haiyang and Rushan relied on fossil fuels for heating supply.
Haiyang Nuclear Power Plant has two reactors in operation. Another two reactors are under construction and are expected to go into operation in 2027. Reactors five and six are in the planning phase.
Wang Linhui, an executive with the company's department of chemical and environmental protection, said that a pump station for heating supply is being built for reactor No 3.
"We are striving to achieve a state of readiness for providing heat to Qingdao by the conclusion of next year," he said. In addition to delivering notable environmental benefits, the heating supply project has significantly enhanced energy utilization efficiency by harnessing heat that would otherwise have been released into the environment.
Wang said the Haiyang plant is also utilizing wastewater at a lower temperature in a mangrove planting initiative. Over 10,000 Kandelia obovata, a species of mangrove tree, have been planted.
Mangroves exist mainly in coastal areas south of 30 degrees north latitude. Despite Haiyang city being around 37 degrees north latitude, the initiative maximizes the use of thermal discharge to warm up the waters where the mangroves are planted.
Shelters have been built to protect the plants from the harsh winter conditions, ensuring their survival, Wang said.
"Over time, these mangroves are likely to acquire cold-resistant traits, and then they may be able to engage in extensive breeding," he said.
Mangroves provide flood protection and reduce erosion in coastal areas.
According to Shandong Nuclear Power Co, the No 5 and No 6 reactors at Haiyang are expected to be completed and put into operation in 2032. By then, the plant's annual power generation capacity will reach 60.9 billion kilowatt-hours, enough to meet the electricity needs of 70 million people.
It will help save standard coal consumption by almost 18.6 million tons, and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 48.63 million tons, which is equivalent to planting 134,000 hectares of broad-leaved forests, Shandong Nuclear Power Co said.